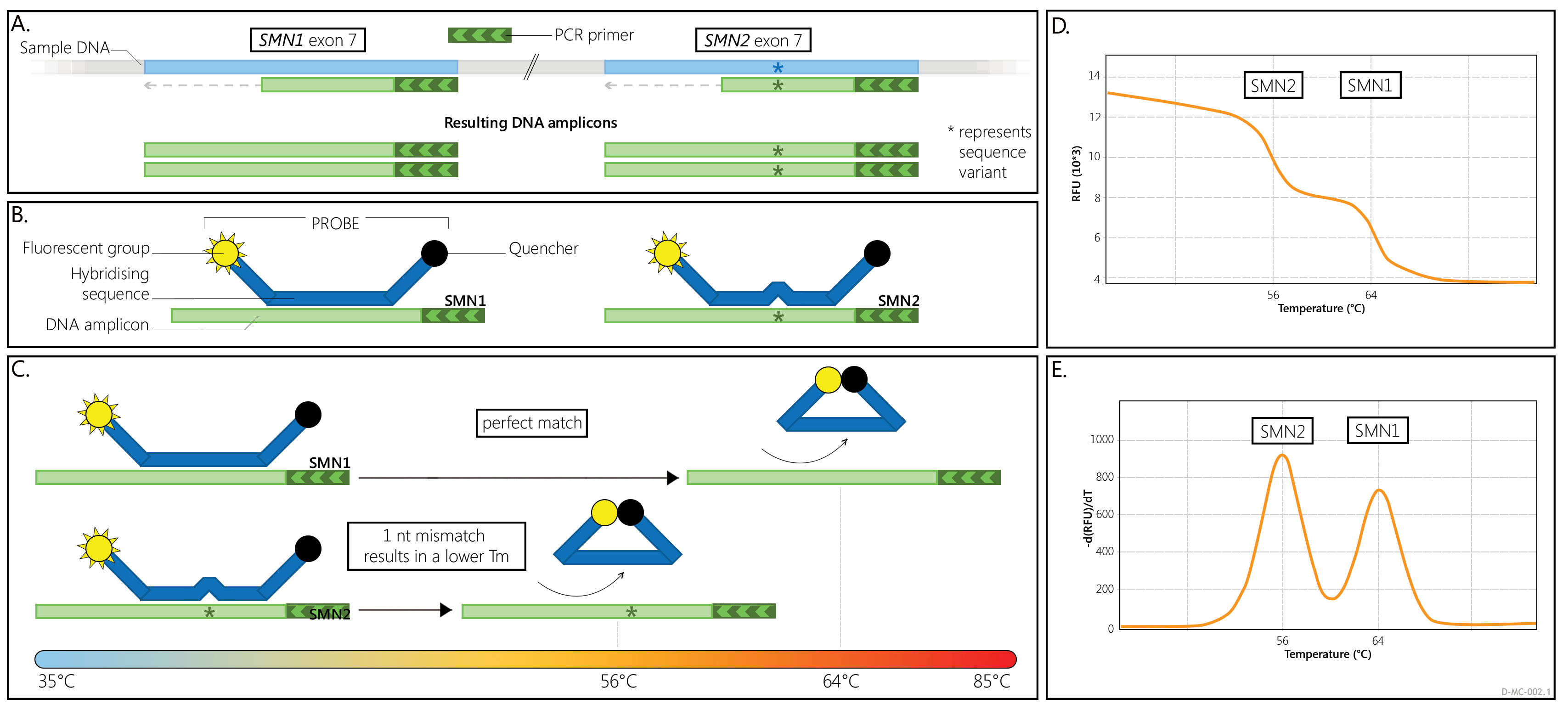
SALSA MC002 SMA Newborn Screen provides information on the presence or absence of SMN1 and SMN2 exon 7 specific sequences in a sample. The relative ratio of the SMN1- and SMN2-specific melt peaks reflects the ratio between SMN1 and SMN2 copies in the DNA sample tested. This means that a sample with two copies of both SMN1 and SMN2 will give the same ratio as a sample with only one copy of both SMN1 and SMN2. No carriers are identified with the MC002 assay as it cannot determine absolute SMN1 or SMN2 copy numbers with the exception of 0 copies.
In the assay a single PCR primer pair is used to amplify a 180 nt fragment of the SMN1 and SMN2 genes that includes exon 7. Formation of at least one of these amplicons is expected in all samples as the complete absence of both the SMN1 and SMN2 genes is incompatible with life. In the MC002 PCR reaction, a larger amount of one primer is supplied compared to the other PCR primer. As a result, one strand is formed in excess (asymmetric PCR) (Figure 1A).
A 5' Cy5 fluorescently labelled oligonucleotide probe is also present in each reaction. This fluorescent probe does not affect the PCR reaction. When the probe oligo is free in solution, probe fluorescence is negligible as there is a specific quencher moiety bound to the 3' end of the probe. When the probe oligo is hybridized to a complementary SMN1 or SMN2 amplicon strand, the Cy5 dye and the quencher molecule are separated, resulting in maximal fluorescence.
After the PCR reaction, the reaction temperature is lowered and the fluorescent probe hybridizes to the SMN1 and SMN2 amplicon strands that were produced in excess, resulting in high fluorescence (Figure 1B). When the reaction mixture is slowly heated, the probe will detach from the amplicon strands at a certain temperature (Figure 1C). This is referred to as the "melting temperature" (Tm) and it is dependent on the sequence of the PCR amplicon.
While slowly heating the reaction mixtures, the fluorescence is measured. The Tm of a probe on a specific sample DNA is identified by a rapid drop in fluorescence during the gradual heating of a sample. These are seen in the so-called melt curve (Figure 1D). A derivative of these melt curves is often used to visualize the Tms as peaks (Figure 1E).
The MC002 probe forms a perfect amplicon-probe hybrid with amplicons that contain the SMN1 exon 7 wildtype sequence resulting in a Tm of approximately 63°C. When bound to an SMN2 amplicon, the probe-amplicon hybrid has a 1 nt mismatch, resulting in a Tm that is approximately 7°C lower (~56°C).
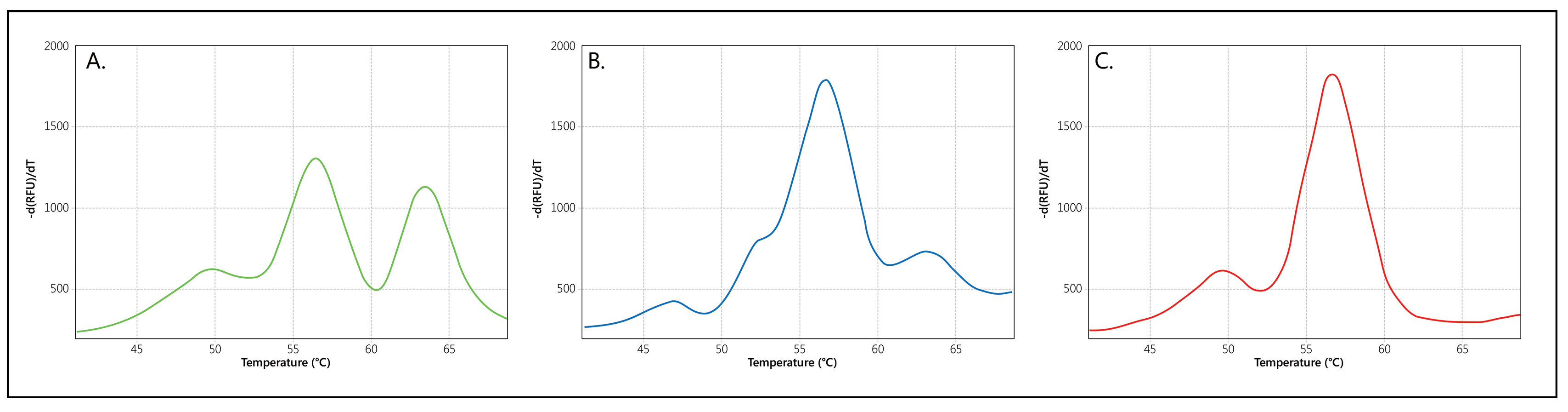
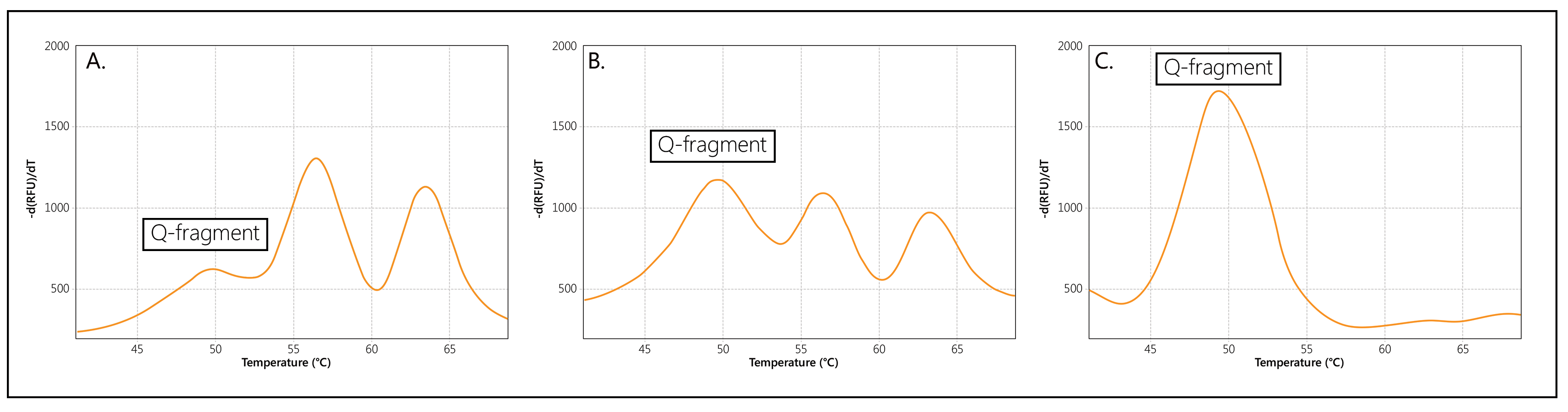
When copies of both SMN1 and SMN2 are present, two separate Tms will be generated for the probe, visualised as two separate peaks (Figure 2A). If only copies of SMN1, or only copies of SMN2, are present in a sample, a single Tm/peak will be generated. Please note that an extra, Q-fragment specific peak with a clearly lower Tm (49°C) may be visible in reactions that contain a low amount of sample DNA.
Melt curve profiles obtained are compared to the melt curves obtained on the SALSA SD074 Threshold DNA known to have a single SMN1 copy and five SMN2 copies (Figure 2B). Samples where the SMN1 peak is absent, or the SMN1:SMN2 peak ratio is lower* as compared to the SALSA SD074 Threshold DNA, must be further tested by an independent technique, such as SALSA MLPA Probemix P021 SMA. SALSA SD075 gives an example of what a SMA patient profile would look like (Figure 2C). The number of samples requiring further testing in newborn screening programs is expected to be below 0.2%.
* A very low SMN1-specific melt peak might be due to contamination of a sample with DNA from another sample. For this reason, not only samples where the SMN1 peak is absent, but also samples with a very low SMN1 peak should be further tested.