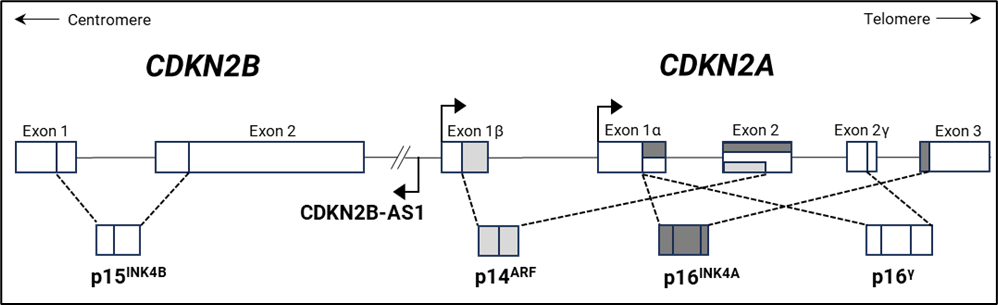
The SALSA MLPA Probemix ME024 9p21 CDKN2A/2B region is a research use only (RUO) assay for the detection of aberrant methylation of one or more sequences of the CDKN2A and CDKN2B genes on chromosome band 9p21. This probemix can also be used to detect deletions/duplications in the aforementioned chromosomal region including MIR31, MTAP, CDKN2A and CDKN2B genes, and PAX5 gene on 9p13.
Genomic losses of the 9p21.3 region, encompassing the CDKN2A/2B genes, are frequent events in many human cancers. This locus encodes three cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p14ARF, p15INK4B and p16INK4A. Genomic deletion of one or both copies of these important cell cycle regulatory genes is the main inactivation mechanism in various cancers. CDKN2A deletion can extend to the MTAP gene, located 110 kb downstream. The MTAP gene encodes methylthioadenosine phosphorylase, an important enzyme for the salvage of both adenine and methionine. It is known that many tumour cells require addition of methionine to their growth medium, because their MTAP gene is co-deleted with CDKN2A. Cells lacking MTAP are expected to be sensitive to purine synthesis inhibitors and/or methionine starvation, and therefore homozygous co-deletion of the CDKN2A and MTAP genes might open possibilities for alternative treatment for cancer patients. Other genes that are frequently co-deleted with CDKN2A/2B are CDKN2B-AS1, PAX5, and microRNA 31 (MIR31). Loss of MIR31 has been shown to have pro-tumorigenic effects on e.g. breast and ovarian cancer (Creighton et al. 2010). CDKN2B-AS1 (non-protein coding CDKN2B antisense RNA 1) is suggested to act as an epigenetic silencer of the CDKN2B gene (Yu et al. 2008). The PAX5 gene, at 9p13, which is essential for normal B-cell lymphopoiesis, is frequently co-deleted with CDKN2A in B-ALL (Kim et al. 2011).
An alternative mechanism of inactivation of the CDKN2A/2B genes is hypermethylation of the promoter regions leading to lack of expression of p14ARF, p15INK4B and p16INK4A proteins, which further results in uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumour development and progression (Wolter et al. 2001).
Alterations of the CDKN2A/2B genes have been also described at the germline level. Germline mutations in the CDKN2A gene are frequently associated with predisposition to malignant cutaneous melanoma and pancreatic cancer (Chan et al. 2021). Up to 40% of familial melanomas are associated with CDKN2A mutations (Hewitt et al. 2002), including point mutations and various intragenic deletions.
The image below shows a schematic representation of the CDKN2A and CDKN2B gene structure and encoded proteins.