Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is an autosomal recessive disorder, which results from a deficiency in one of the enzymes involved in cortisol biosynthesis. CAH affects approximately 1:5,000 births, and among the general population the carrier frequency is estimated at 1:35. In ~95% of cases, CAH is caused by deficiency of the steroid 21-hydroxylating enzyme encoded by the CYP21A2 gene. The inactive pseudogene CYP21A1P is located closely upstream of CYP21A2. Both the gene and pseudogene have 10 exons and span ~3.2 kilobases (kb). The great majority of the CYP21A2 mutant alleles arise through recombination between CYP21A2 and CYP21A1P. In most populations ~65-75% of the pathogenic CYP21A2 mutations are point mutations or small indels, the far majority (>90%) of which are microconversions where the CYP21A2 gene has obtained a single small inactivating mutation from the CYP21A1P pseudogene. The frequency of large deletions and large conversions ranges from ~10 to 35%, two-thirds of which originate from unequal meiotic cross-overs resulting in intergenic deletions of 30 kb and the formation of a CYP21A1P-CYP21A2 chimeric non-functional gene.
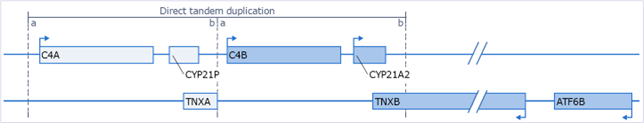
Other genes located in this chromosomal region, also referred to as RCCX module, are the closely related complement genes C4A and C4B, and the TNXB gene and its pseudogene TNXA. Some large rearrangements in this region affect both CYP21A2 and TNXB. Orientation of these genes is as displayed in Figure 1. When both functional alleles of CYP21A2 and both alleles of TNXB are lost this leads to the contiguous gene syndrome CAH-X, where the patient develops symptoms of classic-like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (a disorder affecting the connective tissues) in combination with CAH. Note that for the detection of deletions or duplications in the TNXB gene the SALSA MLPA Probemix P155 EDS is recommended.